マルス| MARS 日本鐵路磁氣自動席位預約系統
車票記載内容【1】
Information on a Ticket – Part 1
1 |
簡介
Introduction
日本擁有全世界最複雜全面的綜合票務系統之一。此票務系統容許乘客在日本各地購買全國的車票,兼且提供乘客一系列的不同票務與出行選擇,其便利與彈性領先地位依然無與倫比。
磁氣自動席位預約系統(簡稱 マルス MARS)在1960年代由日本鐵道部門研發,以應付日益增長的車位預約需求。這個系統減低了票務上的工序,尤其是在其他車站始發的列車。這個系統也有效減低了重複售賣座席的風險。時到今天,系統涵蓋整個日本旅客鐵道網絡,以及不少的第三鐵道部門與私人鐵道公司的網路,能夠為網絡提供多不勝數的票務服務與車票種類,例如販售基本乘車券,急行券,綠色車廂券,指定席與非指定席券,周遊列車票與寝台券等等,也有有限度售賣國内機票與博物館入場票的功能。
以下將會介紹主力介紹遊客經常接觸為JR系統販售的磁氣基本乘車券與指定席券的資訊,其票面顏色為藍色。本文不會討論短途金額票(其票面為橙色)
Japan holds one of the most complicated yet comprehensive integrated ticketing systems in the entire world. This ticketing system allows ticketing to happen across the JR network as well as providing passengers with unrivaled flexibility with ticketing and route planning.
MARS, or Magnetic-electronic Automatic Reservation System, was developed in the 1960s to cope with increasing amounts of seat reservations across the JR network. The system reduced the time and work required to issue tickets, especially ones not originating from the station it was purchased from. It also reduced the likelihood of the same seat being sold twice. Nowadays, this system covers the entirety of the JR network, as well as some third-sector and private railways, and is capable of issuing a wide array of tickets, including Basic Fare, Express, Green, Reserved and Non-Reserved, Cruise and Sleeper tickets, as well as some domestic Boarding Passes and Museum ticketing.
This article will focus on Basic fare and Seat Reservation tickets issued for JR trains issued using MARS (Blue Tickets). This article will not cover Fixed-Fare tickets issued in short distance ticket machines (Orange Tickets).
2 |
基本乘車券
Basic Fare Tickets
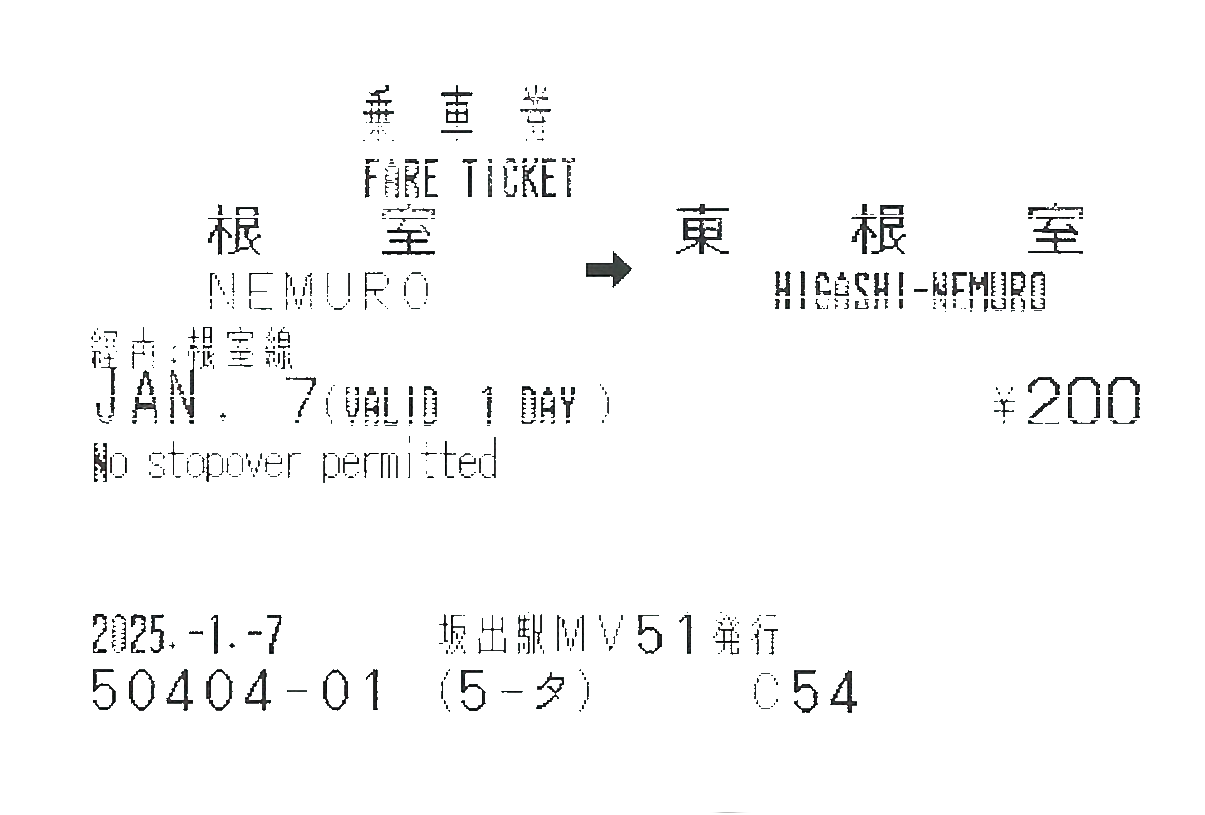
一張由一部MV50指定席售票機外語介面購入的基本車票 A Fare Ticket purchased using a MV50 Reserved Seat Machine’s English Interface
基本乘車券是磁氣自動席位預約系統中最基本的票種。他容許一位乘客自由乘坐任何行駛在票面記載的線路的列車,完成票上的車程。當中,此票對於使用的時間以及發行地點,使用方法等等有極少的限制,唯獨如果需要乘坐特別列車或急行列車,則必須配上一張相對應的額外車票。
The basic fare ticket is the most basic form of ticket offered using the magnetic-electronic automatic seat reservation system. It allows it’s holder to complete a journey originating and ending in the described station by taking any train running on the line specified during it’s period of validity. The restrictions on it’s use are it’s sale are comparatively low compared to other countries, although boarding special trains and express trains will require an additional ticket.
3 |
指定券
Reserved Seat Tickets
指定卷是磁氣自動席位預約系統當初研發的初衷以及繼續生存的使命。一張座席指定卷可能是一趟旅程舒適的關鍵。值得注意是,即便座席指定卷是獨立收費的一張票卷,大部分情況下會與急行,特急或超特急(新幹線)卷一起打印在同一張票卷裡。
其實,無論是與特急卷綑綁或獨立分開,其功能大部分一致。即便在資訊科技發達的年代,車長可以經過手提終端機查詢座位是否已被預約,也會有需要人手檢票的需要,此時,一張已經被打印出的指定卷為唯一已購票的證據。
The reserved seat ticket is the original motivation behind the magnetic-electronic automatic seat reservation system. Just this one ticket could make or break the comforts of a trip. It should be noted that although this ticket embodies a separate fare, it is most often issued on the same piece of ticket as a express surcharge ticket.
No matter attached or detached, the ticket serves the same purpose. In an world where information about a seat’s sale could easily be retrieved through an handheld terminal, a printed ticket still remains the only resilient proof that you have purchased the seat.
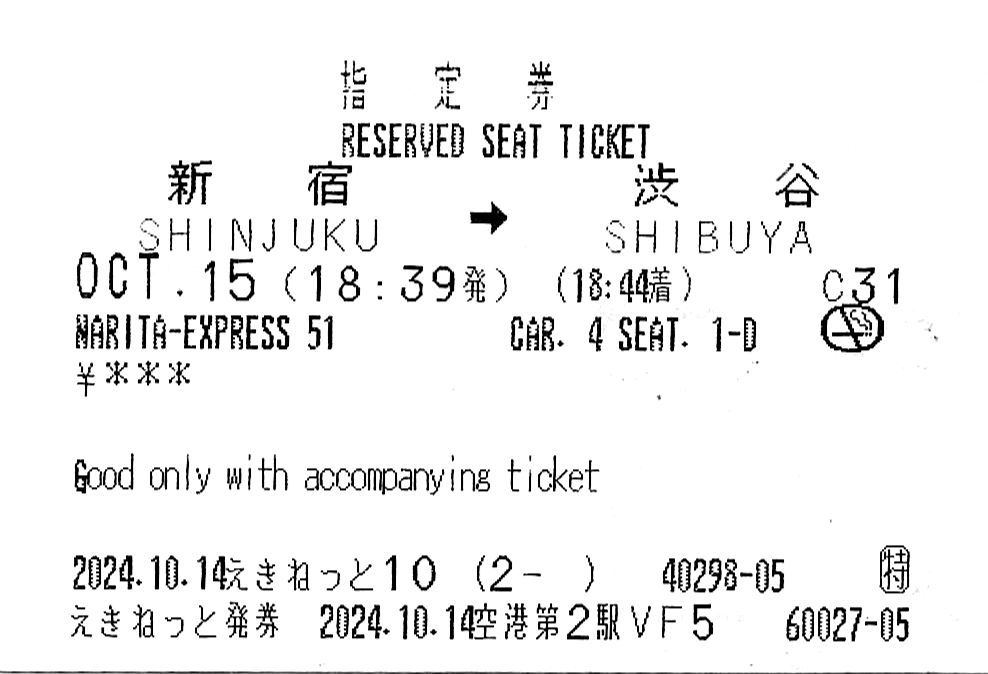
一張由一部MV50指定席售票機外語介面運用東日本網上座席予約系統發行的周遊卷座席指定票 A Reserved Seat Ticket issued by Ekinet (JR East Train Reservation) for an JR East Rail Pass printed using a MV50 Reserved Seat Machine’s English Interface
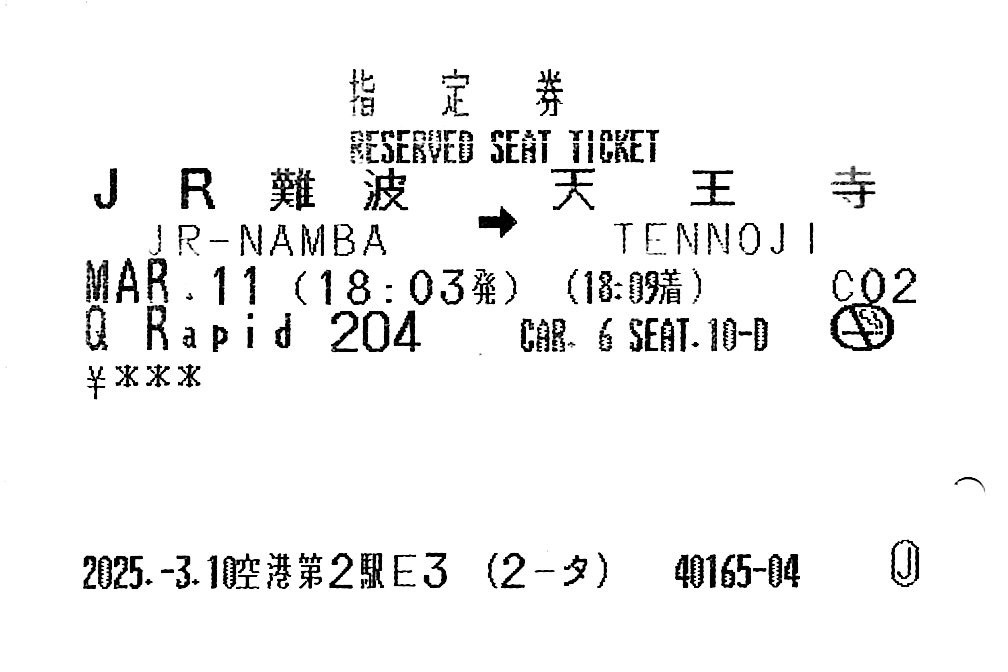
一張由一部ME4業務終端機為日本周遊卷發行的座席指定票 A Reserved Seat Ticket issued by a ME4 Staffed Terminal for a JR Pass
無論是用周遊卷或者自費購買,由於票面記載著列車的具體資訊,車長檢票時也不時會蓋上列車獨特的蓋章,蓋章上印證著乘車時地,車型等獨一無二的旅遊痕跡,也因此成為許多旅客的珍藏紀念品。此獨特的票卷在電子客票日漸成熟時,依然有力抵抗著被電子化的前途,也在二零二四年在擁有電子劃位系統線路上保持著主流地位。
No matter how the ticket was obtained, through a purchase or as part of a rail pass, it is filled with detailed information about the train ride. Occasionally, the conductor will stamp the ticket with validation stamps oftentimes unique to the service. Because of the physical marks of travel, the reserved seat ticket became an irreplaceable part of a traveler’s collection. And in an increasingly ticket-less world, the reserved seat ticket remains fiercely defiant to being digitalized, with physical tickets remaining mainstream on lines that do offer digital reserved seat ticketing in 2024.










Leave a Reply